LLM Reverse Engineering with RAG to Probe AI Search Behavior
July 06, 2025
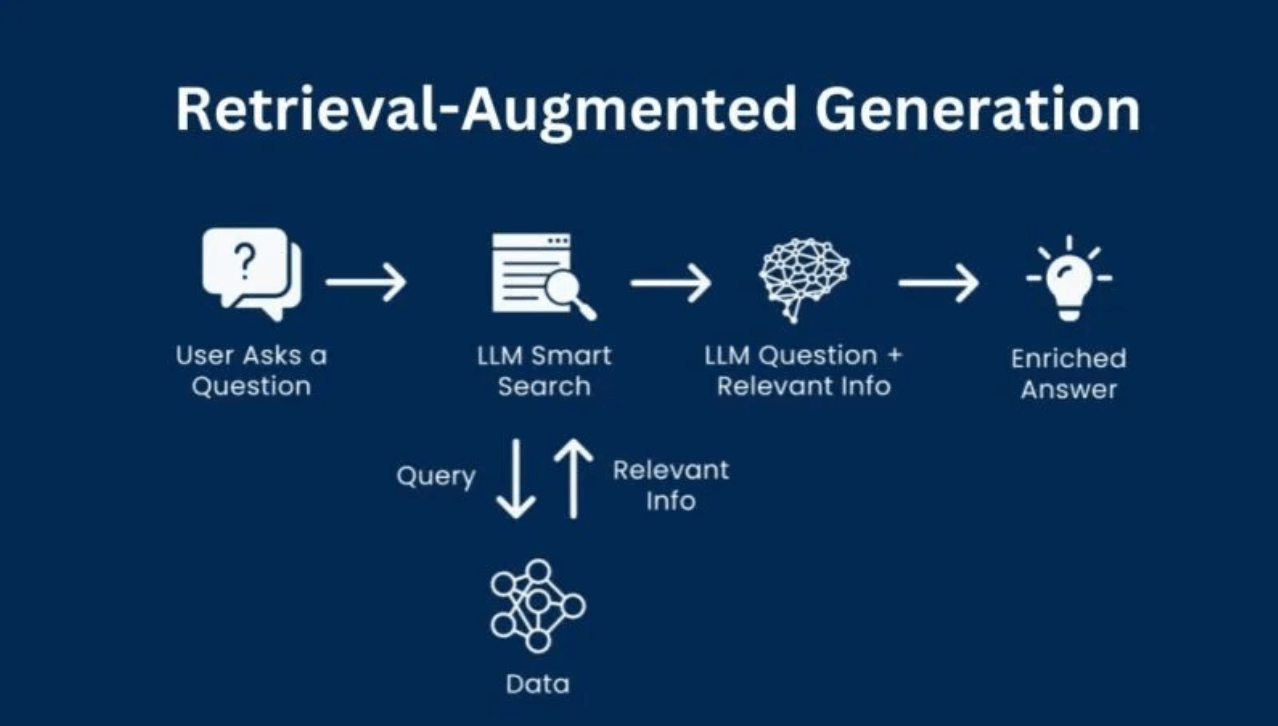
Note: RAG is a technique that improves an LLM’s capabilities by integrating them with external data sources.
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) systems can be used to simulate and test how LLMs retrieve content. They don’t just probe what a model knows, but what it displays when someone asks a question.
So here’s a simple experiment. Use ChatGPT’s search mode to run a query, copy the full text of the cited sources, and load them into a local RAG pipeline built with n8n. From there, start asking questions against the dataset and watch what the model pulls up. You can make small tweaks like changing headings, rephrasing sections, or adding new pages to see what ripple effects occur.
What you can learned by rebuilding the retrieval stack
The first big insight here is that LLMs won’t retrieve entire webpages, they will pull chunks… of paragraphs and sections. If the right terms aren’t in the right block of text, the model won’t select it—even if the broader page is relevant.
Next, you’ll note that the Q&A structures perform really well even if they’re not FAQs. If a page has summaries, question-like subheadings, or bullet-point answers, the model is much more likely to grab and reuse that text.
But keywords still matter. Not so much across the page but in the chunks. If a keyword or phrase isn’t embedded in the local context, an LLM might skip it entirely. In other words, the idea of keyword density is not the focus here.
Why RAG matters for reverse engineering
RAG gives you a lab environment to test how AI might respond to real-world questions. You control the content and the prompt. You also get to see which chunks rise to the top.
It’s not a perfect mirror of live LLM behavior, but it’s helpful enough to reveal certain patterns:
-
Which types of structure improve extractability
-
What phrasing improves retrievability
-
How small edits shift the model’s attention
RAG is a smart way to test your content’s influence without having to access the internal workings of a proprietary LLM.
What comes next
Retrievability is just as important as relevance here. You may write brilliant, on-topic content but still be invisible to AI if the structure doesn’t fit with chunk-level extraction.
Next up in this series, I’ll look at how prompts, citations, and retrieval context shape what LLMs decide to surface—and how that impacts your ability to show up in chat-based interfaces.